Finasteride For Hair Loss: Dose, Results, And Side Effects
You will be surprised to learn how this FDA-approved drug benefits your locks.
Image: Shutterstock
Finasteride for hair regrowth has taken the world by storm. It is a prescription drug used in small doses to treat androgenic alopecia (1). Androgenic alopecia is a common cause of hair loss in men and women. It affects about 50 million men and 30 million women in the US (2). Many factors cause hair thinning and hair loss – genetics, diet, stress, hormones, etc. Finasteride has shown promising results in combating hair loss. But, is it safe? What are the side effects of this hair loss medication? Read on to get all the answers along with scientific data. Scroll down!
 Know Your Ingredient: Finasteride
Know Your Ingredient: FinasterideWhat Is It?
A medication used to treat the symptoms of hair loss and enlarged prostate in men.
What Are Its Benefits?
It can reduce the risk of female and male pattern hair loss.
Who Can Use It?
It should not be taken without the proper consultation of your doctor.
How Often?
The dose and frequency of the medication depend on your healthcare provider.
Caution
It can cause erectile dysfunction, decreased sexual desire, swelling of breast tissues in men, and low blood pressure.
In This Article
What Is Finasteride And How Does It Work?
Finasteride is an FDA-approved prescription drug used for treating androgenic alopecia. It works by inhibiting the conversion of testosterone, the male sex hormone, to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) (3). High levels of DHT shrink the hair follicles and shorten the hair cell growth cycle, making hair prone to falling (4). The drug may be an effective hair loss therapy to reduce the risk of female pattern hair loss in women and male pattern hair loss in men.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?But is this mechanism backed by any scientific evidence? Read on to know what research has to say about finasteride as a treatment for hair loss.
What Does Research Say About Finasteride For Hair Loss?
Finasteride, in laboratory experiments, has shown to reduce male pattern baldness (‘M-shaped’ balding) in men and female pattern baldness (thinning of hair throughout the scalp) in women. Let us have a quick glance at those studies.
Japanese scientists tested the effect of 1 mg Finasteride on 2,561 Japanese men with androgenic alopecia (male pattern baldness). Hair count increased greatly in 11% men, moderately in 36.5% men, and slightly in 39.5% men. Also, the response rate had improved with an increase in the treatment duration (5).
Another study by American scientists found that 1 mg/day of finasteride slowed hair loss and boosted hair growth in men over a 2-year treatment period (6). A review paper in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology observed that topical application of finasteride decreased plasma DHT in men and women (7).
Sixty-five men with androgenic alopecia were treated with a combination of finasteride 1 mg/day and topical application of 5% Minoxidil. Both the medications could treat mild to severe male pattern baldness (8).
Excessive testosterone production in some women may lead to irregular periods, hirsutism (hair on the face, chest, and back), and androgenic alopecia (9). Finasteride is not effective and possibly dangerous for women of childbearing age. However, a 67-year-old lady without hyperandrogenism (excess body testosterone) showed significant hair growth when treated with finasteride 5 mg for a year (10).
In another study, 37 pre-menopausal women were administered with 2.5 mg finasteride and an oral contraceptive. 62% of the patients showed a reduction in hair loss. Finasteride 5 mg/day administered to 87 pre-menopausal women for a year showed increased hair thickness and density in a separate study (11).
Finasteride, alone or with minoxidil, is an effective drug for treating male pattern baldness. However, more studies on women with larger sample sizes are warranted (considering their menopausal and hyperandrogenism status). But at what optimal dose does finasteride work? Keep reading to find out.
Finasteride Dose To Reduce Hair Loss
1 mg of finasteride is the prescribed dose for androgenic alopecia or hair fall in men and women. Clinical studies have also shown that 1 mg of finasteride per day can promote hair growth and prevent further hair loss in men (12). But how long should you take finasteride to see results? Find out in the next segment.
How Long Does It Take To Work?
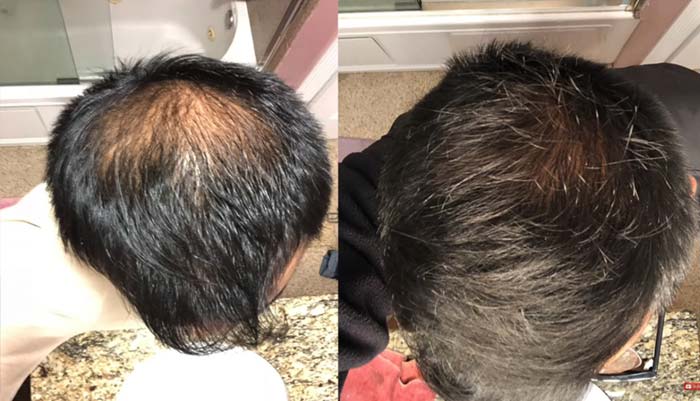
According to the studies mentioned above, finasteride may take a year or two to show significant results. Talk to your doctor to chart out a treatment course that is most beneficial for you. Here are a few before-and-after pictures of results from finasteride treatment.
Finasteride Hair Growth Results
While low doses of finasteride may help with hair regrowth and improve hair density, the drug does come with its set of side effects. We have discussed the same in the following section.
Side Effects Of Finasteride
Here are a few side effects finasteride may cause (3), (13), (14):
- Erectile dysfunctioni XA condition where men have trouble maintaining an erection firm enough for sexual intercourse. .
- Decreased libidoi XAn individual's overall sexual desire or urge, impacted by psychological, biological, and social aspects. .
- Gynecomastia, or swelling of breast tissues in men.
- Orthostatic hypotensioni XLow blood pressure that occurs when you stand up after sitting or lying down, causing dizziness. , or low blood pressure as one stands up.
- External genital deformity in male offspring.
Note: The side effects may continue despite the discontinuation of the therapy (also called post-finasteride syndrome) (3).
Can Women Take Finasteride?
Women of childbearing age should avoid taking finasteride as it increases the risk of external genital deformity in male offspring (15). Pre-menopausal and/or post-menopausal women can go for doctor-prescribed finasteride for reducing androgenic alopecia, only if other treatment options are not effective.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipInfographic: Everything To Know About Finasteride For Hair Loss
Hair loss is common across all ages and genders. Although a little hair fall here and there is natural, severe hair loss can be very distressing. One way to address this issue is the use of Finasteride as a treatment. Check out the infographic below to learn all about using this prescription drug.

Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Save the high-quality PDF version on your device now.
Download Infographic
Hair loss is a common hair issue faced by all people of all genders. It affects your self-esteem and social life. One of the treatments recommended to manage and reduce hair loss is finasteride. While you can use finasteride for hair restoration, there are some side effects that it may cause.
Lactating and pregnant women should steer clear of this drug. They can try the PRP treatment instead, which shows results in 6 months to a year. To promote healthy hair growth naturally, you should focus on eating healthy, exercising daily, sleeping well, and stress relief. Following a regular hair care regimen with steps like oiling your hair can promote hair growth.
Since it has adverse effects, you can try other natural alternatives and some natural hair loss remedies that are healthier and safer. These alternatives and remedies work effectively without causing side effects. These natural ingredients contain anti-androgenici XA substance or property that interrupts the synthesis, functioning, and effects of testosterone and other male sex hormones. properties that can aid in hair loss prevention. But, you should use these anti DHT-blends with caution.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is taking finasteride worth the risk?
Finasteride is generally safe to consume. However, there are a few side effects that have been reported in relation to finasteride. Though it helps regrow your hair, it may cause side effects like erectile dysfunction, decreased libido, and gynecomastia. Be aware of these side effects to make an informed decision.
Do celebrities use finasteride?
Yes, celebrities do use finasteride. Celebrities like Pete Davidson have used finasteride to treat hair loss.
Will finasteride regrow hairline?
Yes, using finasteride can help regrow hair around the hairline. It can also help stop receding at the temples.
Is finasteride better than minoxidil?
Finasteride is said to be more effective than minoxidil. However, a combination of both can also help treat hair loss issues.
Can I take finasteride for a lifetime?
Yes, it is safe to use finasteride throughout your life. However, check with your doctor to determine the dosage.
Does finasteride cause white hair?
Finasteride does not cause white hair. However, a person with light gray or white hair may notice a grayish or yellowish tinge while using it.
Key Takeaways
- Finasteride is an FDA-approved medication used for treating androgenic alopecia in men and women.
- Studies indicate that taking 1mg of finasteride daily slows down hair fall and stimulates hair growth.
- Women of reproductive age should avoid taking finasteride as it may increase the risk of external genital deformity in male children.
Learn how to use finasteride for BPH and hair loss. Get the facts on doses, side effects, and more. Check out the video below!
Sources
- Androgenetic alopecia.
https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/androgenetic-alopecia/#frequency - Guidelines on the use of finasteride in androgenetic alopecia.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26924401/ - Finasteride
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513329/ - Evaluation of efficacy and safety of finasteride 1 mg in 3177 Japanese men with androgenetic alopecia.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21980923/ - Androgenetic Alopecia in Women.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022202X15529369#:~:text=Androgenetic%20alopecia%20(AGA)%2C%20also,the%20same%20as%20in%20men. - Finasteride in the treatment of men with androgenetic alopecia. Finasteride Male Pattern Hair Loss Study Group.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9777765/ - A Systematic Review of Topical Finasteride in the Treatment of Androgenetic Alopecia in Men and Women.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6609098/ - An open, randomized, comparative study of oral finasteride and 5% topical minoxidil in male androgenetic alopecia.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15316165/ - Alopecia in Women.
https://www.aafp.org/afp/2003/0301/p1007.html - Finasteride for Hair Loss in Women.
http://www.dpic.org/article/professional/finasteride-hair-loss-women - Hormonal therapy in female pattern hair loss.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5419033/#:~:text=However%2C%20one%20study%20of%2037,et%20al.%2C%202006). - Finasteride: a review of its use in male pattern hair loss.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9951956/ - Controversies in the treatment of androgenetic alopecia: The history of finasteride.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30253001/ - Finasteride: a review of its use in male pattern hair loss.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9951956/ - Finasteride and Its Potential for the Treatment of Female Pattern Hair Loss: Evidence to Date.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7060023/ - Finasteride: Does it affect spermatogenesis and pregnancy?
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2018472/pdf/11785276.pdf - The benefits of finasteride for hirsute women with polycystic ovary syndrome or idiopathic hirsutism.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12724020/